When creating a rule, this window lets you:
- customize the response to an event by selecting a program to be executed (Specify Program for Action)
- specify an action taken when a rule action is undone (Specify Program for Undo)
In either case, the information you configure is the same for both windows, the only difference is the title of the window. The window is accessed from the ASM Configuration Window's Rule Definitions view.
Click areas in the window for more information.
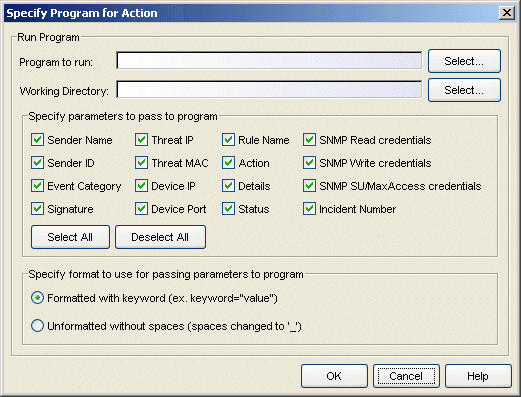
- Program to run
- This field defines the script launched for this Custom Action
or Custom Undo. Scripts are stored in the <install directory>\appdata\AutoSecMgr\scripts directory. Type a script name, if known, or use the Select
button to open a file browser window and choose a script.
You can not use options with the Program to run field. For example, you cannot enter myscript.bat -i <IP Address> -m <MAC Address> in the Program to run field.
TIP: To execute a script with options, create a script without options that executes another script with options (Windows only). For example: - Create a script named, asm_script.bat with an entry to call myscript.bat such as:
C:\Program Files\My Custom Files\myscript.bat -i %1 -m %2". - Uncheck all but the Threat IP and Threat MAC checkboxes and select Unformatted without spaces (you don't want to send any keyword (thip= or thmac=) to your script.). The variable %1 returns <Threat IP Address> and %2 returns the <Threat MAC Address>.
If you are using PERL script, use a different argument variable, such as $ARGV[0] (First argument) or @ARGV (all arguments). Also, using the shell script is similar to a Windows batch file script (%1 for the first argument, %* for the all arguments).
- Create a script named, asm_script.bat with an entry to call myscript.bat such as:
- Working Directory
- This is the path to the directory from which the script is executed. Any path references within your script that are not absolute paths, are relative to this directory. Enter a path or use the Select button to open a file browser window and choose a directory.
- Specify parameters to pass...
- These check boxes let you select elements of the event information that are passed as parameters to your program. The Select All button places a check in all of the boxes and the Deselect All button removes checks from all of the boxes.
- Specify format to use...
- This area lets you select the format used to pass the selected parameters to your program:
- Formatted with keyword...
- When selected, the parameters are passed using a format that includes a keyword associated with each parameter (e.g., keyword="value"). So, for example, if Sender Name is selected as a parameter, the keyword sname is used and the information passed to the script is sname="dragon_id" followed by a space and then the keyword and value for the next parameter. The following table defines the keywords for each parameter and the order that the values are passed to the script (listed from top to bottom in the table).
Parameter Keyword Sender Name sname Sender ID sid Event Category ecat Signature sig Incident Number incident Threat IP thip Threat MAC thmac Device IP dev Device Port port Rule Name rname Action action Details dtls SNMP Parameters see Note 1 Status stat Note 1: When you select any SNMP parameter, the snmp=value indicates the SNMP version and the subsequent parameters contain the values assigned for the credentials associated with the device. When you select multiple SNMP parameters (e.g., SNMP Write and SNMP Read) the script uses the values for the highest access level.
SNMP v1, SNMPv2 SNMPv3 Parameter Keyword Parameter Keyword SNMP Read snmp="v1"
roSNMP Read,
SNMP Write,
SNMP SU/Max Accesssnmp="v3"
user
seclevel
authtype
authpwd
privtype
privpwdSNMP Read snmp="v1"
rwSNMP Read snmp="v1"
suExample:
If you select Sender Name, Sender ID, Threat MAC, and SNMP Write and the device is configured for SNMPv1 credentials, the information passed to the script appears as:
sname="my sender name" sid="dragon id" thmac="00.00.1d.11.22.33" snmp="v1" rw="public"
And, for a script named myscript.bat, the resulting script command is executed as:
<install directory>\appdata\AutoSecMgr\scripts\my_script.bat sname="my sender name" sid="dragon id" thmac="00.00.1d.11.22.33" snmp="v1" rw="public"
- Unformatted without spaces...
- When selected, the parameters are passed as space delimited, unformatted text, without keywords. For this option, your script must know which parameters are being passed and the order in which they are passed. If a parameter contains any spaces, they are replaced with an underscore ( _ ).
Example:
You select Sender Name, Sender ID, Threat MAC, and SNMP Write and the device is configured for SNMPv1 credentials, the information passed to the script appears as:
my_sender_name dragon_id 00.00.1d.11.22.33 v1 public
And, for a script named myscript.bat, the resulting script command is executed as:
<install directory>\appdata\AutoSecMgr\scripts\my_script.bat my_sender_name dragon_id 00.00.1d.11.22.33 v1 public
For information on related windows:
For information on related tasks: