VLAN Tab (Device)
The Device view of the VLAN tab enables you to do any or all of the following:
- compare (verify) model VLAN definitions with VLAN settings on devices
- update model VLAN definitions with VLAN settings from devices
- write (enforce) model VLAN definitions to devices
To access the Device view of the VLAN tab, select the device(s) or group(s) of interest in the left panel. Then select the VLAN tab in the right panel and confirm that the Device radio button is selected. The Device view of this tab consists of an upper panel and a lower panel. Use the panel control buttons ![]()
![]() to control the display of the two panels.
to control the display of the two panels.
For more information, see How to Work with VLAN Models.
Click the areas in the window for more information.
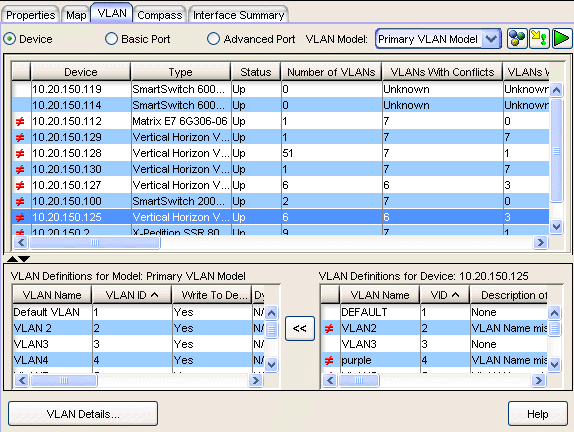
Upper Panel
The table in the upper panel provides VLAN information about the device(s) selected in the left panel. You can compare the current VLAN settings on the selected device(s) with the VLAN definitions in the selected VLAN model by clicking Start Verify (Retrieve) ![]() . Devices on which differences are detected are marked in the table by a red not-equals sign
. Devices on which differences are detected are marked in the table by a red not-equals sign ![]() .
.
- VLAN Model
- Select the VLAN model whose VLAN definitions you want to display in the left table of the lower panel.
Device VLANs Table
This table provides VLAN information for the device(s) selected in the left panel. A red not-equals sign  indicates that there are differences between the VLAN definitions in the model and the VLAN settings on the device(s).
indicates that there are differences between the VLAN definitions in the model and the VLAN settings on the device(s).
| NOTE: | When you create multiple VLAN models, consult the Max VLANs Supported and Max VLAN ID values in this table, and create your VLANs based on the limitations of the device you are configuring. This will help you to avoid enforcing problems arising from conflicts between the maximums in a template and the maximums supported on a device.
|
|---|
- Status
- This column indicates whether or not the device is up or down. Possible values include: Up, Down or Error returned:Timed out.
- VLANs With Conflicts
- Total number of VLANs on the devices that do not match the VLAN settings in the model.
- VLANs With Unsupported Differences
- Total number of VLANs on the device(s) that do not support dynamic egress, IGMP and X-Pedition Protocol when checked in the model.
- Max Supported VLANs
- Maximum number of IEEE 802.1Q VLANs that this device supports. Consult this value when creating VLANs, to avoid enforcing problems arising from conflicts between the number of VLANs in a template and the number of VLANs supported on a device.
- Max VLAN IDs
- Maximum IEEE 802.1Q VLAN IDs that this device supports. Consult this value when creating VLANs, to avoid enforcing problems arising from conflicts between the maximum VID in a template and the maximum VID supported on a device.
- Traffic Classes Enabled
- Indicates whether or not weighted priority is enabled on the device. Possible values are: Enabled, Disabled, Unknown.
- GVRP Status
- Indicates whether GVRP (GARP VLAN Registration Protocol) will be enabled or disabled on the ports using this VLAN.
- IGMP New Default State
- Indicates the IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) state of the device:
- Enabled - IGMP is enabled.
- Disabled - IGMP is disabled.
- Unsupported - IGMP is not supported on the device.
- Unknown - The IGMP state of the device is not known.
- Extended Multicast Filtering Services
- Indicates whether extended multicast filtering services are implemented. Devices that implement this functionality can perform filtering of individual multicast addresses controlled by GMRP (GARP Multicast Registration Protocol). GMRP is a protocol used to register multicast addresses on ports to control flooding of multicast frames. Possible values include: Yes, No, Unknown.
- Traffic Classes
- Indicates whether or not weighted priority is available on this device. Possible values include: Yes, No, Unknown.
- Static Entry Individual Port
- Indicates whether or not static entry individual port is implemented. If Yes, ports from which frames must be received for filtering information to apply may be specified. Possible values include: Yes, No, Unknown
- VLAN Learning
- Displays the filtering database modes of operation implemented by the device:
- IVL -- Independent VLAN Learning
- SVL -- Shared VLAN Learning
- IVL/SVL -- Both Independent and Shared VLAN Learning
- Unknown -- Filtering database mode unknown
See VLAN learning for more information.
- Configurable PVID Tagging
- Indicates whether or not configurable PVID tagging is implemented. Devices that implement this functionality have the ability to override the default PVID setting and the egress state (Tagged or Untagged) on each port. Possible values include: Yes, No, Unknown.
- Local VLAN Capable
- Indicates whether or not the device can support multiple local bridges, outside of the scope of 802.1Q defined VLANs. Possible values include: Yes, No, Unknown.
Lower Panel
The left table in this panel shows the VLAN definitions in the VLAN model selected at the top, and the right table shows the VLAN settings on the device selected in the upper table. You can update the VLAN model with selected device settings, if desired.
Note: Egress Lists on the device are not checked to see if the VLAN will be egressing any ports.
VLAN Definitions for Model
This table displays the VLANs defined for the VLAN model selected at the top of the tab.
- VLAN ID
- VLAN ID) Unique numerical identifier of the VLAN.
- Write to Device(s)
- Indicates whether or not the VLAN will be written to the device(s) when you enforce, or compared to the actual VLANs on the device(s) when you verify (Yes or No).
- Dynamic Egress
- Indicates whether or not dynamic egress is enabled for the VLAN (Yes or No).
- IGMP Status
- Indicates whether IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) is a factor in this VLAN's definition, and if so, if it is to be enabled or disabled:
- N/A - IGMP is not a part of the VLAN's definition.
- Enable - IGMP is a part of the VLAN's definition, and is enabled.
- Disable - IGMP is a part of the VLAN's definition, but is currently disabled.
- IGMP Version
- For VLANs using IGMP, the version of IGMP that will be utilized on ports associated with the VLAN (Version 1,Version 2).
- Switch Query IP
- The address of the IGMP Querier on the IP subnet to which this interface is attached.
- Query Interval
- Interval (in seconds) between general IGMP queries sent by the device. Larger values cause queries to be sent less often. This value must be greater than the Query Response interval. Valid values: 1 through 300. For more information, see IGMP.
- Query Response
- Maximum amount of time allowed for responses to general IGMP queries. Larger values result in less bursty traffic. This value must be less than the Query Interval. Valid values: 1 through 300. For more information, see IGMP.
- Interface Robustness
- (Robustness Variable) Indicates how susceptible the subnet is to lost packets. A higher value may indicate that the subnet is particularly susceptible to losses. For more information, see Interface Robustness.
- Last Member Query Interval
- Maximum amount of time (in seconds) between group-specific query messages, including those sent in response to leave-group messages. Lower intervals reduce the amount of time it takes the device to detect the loss of the last member of a group. See IGMP for more information.
VLANs Definitions for Device
This table shows the VLANs currently defined on the device selected in the upper table. A red not-equals sign  indicates that there are differences between the VLAN model definition and the VLAN setting on the device.
indicates that there are differences between the VLAN model definition and the VLAN setting on the device.
- Description of Differences
- Description of the discrepancies detected between the VLAN definitions in the model and the VLAN settings on the devices. Possible differences include:
- Dynamic Egress is Disabled on Device
- Dynamic Egress is Enabled on Device
- Dynamic Egress is not supported on Device
- IGMP Interface Robustness on device is 100
- IGMP Last Member Query Interval on device is 100
- IGMP not active for VID <number>
- IGMP not enabled on Device
- IGMP not supported on Device
- IGMP Query Interval on device is 100
- IGMP Query Response on device is 100
- IGMP Version on Device is <version>
- VLAN is not in VLAN Model
- VLAN is not on Device
- VLAN Name mismatch for VID <number>
- VLAN Not fully defined on Device
- VID
- Numerical identifier of the VLAN (VLAN ID).
- Type
- Displays the VLAN filtering/forwarding type. Possible values include:
- Permanent - The VLAN is active and will remain so after the next reset of the device.
- GVRP - The VLAN is active and will remain so until removed by dynamic GVRP.
- Other - The VLAN is active, but is not permanent or dynamic GVRP.
- Create VLAN - The VLAN is not on the device and needs to be created.
- Status
- Indicates whether the VLAN is enabled on the device. Possible values include: Enabled, Disabled, Other, N/A.
- Dynamic Egress
- Indicates whether or not dynamic egress is enabled for the VLAN (Yes or No).
- IGMP Status
- Indicates the IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) status of the VLAN:
- Unsupported - IGMP is not supported on the device.
- Not Defined - IGMP is supported on the device, but is not a part of the VLAN's definition.
- Enabled - IGMP is supported on the device, is a part of the VLAN's definition, and is enabled.
- Disabled - IGMP is supported on the device, is a part of the VLAN's definition, and is disabled.
For the definitions of the remaining columns in this table, see VLAN Definitions for Model.
 VLAN Element Editor Button
VLAN Element Editor Button
- Opens the VLAN Element Editor window where you can modify existing VLAN models or create new ones.
-
 Enforce Button
Enforce Button - Writes the VLAN selected in the VLAN Definitions for Model table to the device(s). The VLAN's Write VLAN to Devices property must be set in order for its definitions to be enforced. To avoid unpredictable results, allow the enforce to complete before selecting another tab or device.
NOTE: On the X-Pedition router, enforcing will not overwrite the "System Static" VLAN (SYS_L3_Interface Name). However, you can update a VLAN model definition with the System Static VLAN definition from the router.
-

 Start/Stop Verify (Retrieve) Button
Start/Stop Verify (Retrieve) Button - Compares the selected model's VLAN definitions with the VLAN settings on the selected device(s), and displays the discrepancies in the upper table. Only those VLANs whose Write VLAN to Devices property is set are verified. When you initiate the verification process, this button changes to Stop, and you can stop the verification at any time. If there are no VLAN models against which to compare the device VLAN settings, this button is grayed out. If a difference is detected, a red not-equals sign
 is displayed in front of the appropriate line in the table.
is displayed in front of the appropriate line in the table.
-
 Update (Merge) Button
Update (Merge) Button
- Updates the selected VLAN definition in the VLAN Definitions for Model table with the device VLAN settings selected in the right table. To avoid unpredictable results, allow the merge to complete before selecting another tab or device.
CAUTION: This operation cannot be undone.
| NOTE: | Certain devices that allow the creation of VLANs without VLAN names may create VLANs with blank names in the model. You can rename these if you like, or leave them blank. Either way, these VLANs and their properties (modified or not) will be saved when you click Save.
|
|---|
- VLAN Details
- Opens the VLAN Details window.
For information on related tasks:
For information on related windows: