Use this window to add a new agent-less test set or edit an existing agent-less test set. In the test set you can define certain assessment parameters, such as scanning level and scoring mode, and specify which assessment resources to use. When you add a new test set, it becomes available for selection in the Edit Assessment Configuration window.
To add an agent-less test set, click
![]() (the configuration menu
button in the Test Sets section of the
Edit Assessment
Configuration window) and select Add Agent-less. You can also click
the Add button in the Manage
Test Sets window.
(the configuration menu
button in the Test Sets section of the
Edit Assessment
Configuration window) and select Add Agent-less. You can also click
the Add button in the Manage
Test Sets window.
To edit an agent-less test set, from the
Edit Assessment
Configuration window, click on the agent-less test set you want to edit, then click
![]() (the configuration menu button in the Test Sets section), and
select Edit. You can also click
the Edit button in the Manage
Test Sets window.
(the configuration menu button in the Test Sets section), and
select Edit. You can also click
the Edit button in the Manage
Test Sets window.
Click areas in the window for more information.
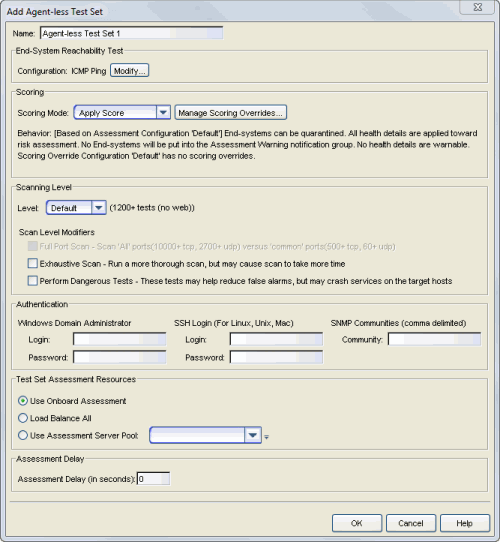
- End-System Reachability Test
- Click the Modify button to open a window where you can select the
type of end-system reachability test that will be
used to verify that the end-system can be reached prior to and following
assessment: ICMP Ping and/or TCP Ping with a list of ports. If neither
test is selected, then there will be no test.
Running either or both tests allows NAC Manager to determine if an end-system is reachable prior to running an assessment. If the end-system is not reachable, the assessment will not be run and the end-system will receive the Failsafe policy. If the end-system is reachable, the assessment will be performed. Without reachability testing, if assessment is required and the end-system is not reachable, the assessment may take significantly more time and you could see a "false positive" in the sense that the assessment would come back without errors, but only because the end-system could not be contacted to do an assessment. In this case, the end-system would be assigned the Accept policy and allowed on the network without an actual assessment taking place.
Another advantage to running end-system reachability tests is that the test is performed before and after an assessment. If test results are different, the end-system will be quarantined. For example, with a TCP Ping test that has 15 ports configured, if any of the ports differ before or after the assessment, the end-system is quarantined. With the ICMP Ping test, if the end-system passes the test before assessment, but fails the test after assessment, the end-system is quarantined.
| NOTE: | For ICMP Ping, how NAC Manager handles the timeout per ping attempt may differ depending on the
operating system on which the Extreme Management Center server is running, however the total timeout period specified will
be the same (e.g. 2 attempts * 5 timeouts = 10 seconds). For TCP Ping, the number of ping attempts
is not specified because it is inherent in the TCP protocol. |
|---|
- Scoring
- The Scoring Mode lets you decide how the score returned by an assessment test
will be used:
- Apply Score - Test score results will be included as part of the quarantine decision, and end-systems can be quarantined.
- Informational - Test score results will be reported, but are not applied toward a quarantine decision. This allows you to use assessment as a data-gathering mechanism without end-systems being quarantined or warned.
- Warning - Test score results are only used to provide end user assessment warnings via the Notification Portal web page. No end-systems will be quarantined unless a grace period (if specified) has expired.
Scoring overrides can be used to change the scoring mode for specific tests. For example, you may set a scoring mode of "Informational" and then configure scoring overrides to set specific tests to count towards a quarantine decision. Or, you may select a scoring mode of "Apply Score" (quarantine), and then create scoring overrides to set specific tests to be warnings. Use the Manage Scoring Overrides button to open the Manage Scoring Override Configurations window where you can view and define your scoring overrides.
The text below the Scoring Mode selection describes the behavior that will result from the current scoring mode and any scoring override settings. Since a test set can be used in different assessment configurations, this description is based on the assessment configuration that is currently open.
- Scanning Level
- The agent-less assessment can be configured to assess end-systems at
various levels of intensity. Light assessments will be faster but will not
gather as much information as heavy assessments.
- Light - The assessment collects information from the DNS (Domain Name System), tries to identify the operating system, and tries to establish what RPC (Remote Procedure Call) services the end-system offers and what file systems it shares via the network.
- Default - This scanning level scans roughly 600 ports and performs around 1,200 tests.
- Heavy - At this level, the scan checks for services listening on any TCP port from 1 to 10,000, and any UDP port from 1 to 2,050, with the exception of WinNT ports which are known to cause certain software to crash when scanned. Any services detected will then be scanned for any known vulnerabilities. It performs roughly 2,750 tests.
- Custom - This scanning level lets you run a custom Saint scan. Enter the custom scan file. For information on creating a custom scan see How to Create a Custom Scan for Agent-less Assessment.
- Scan Level Modifiers
- Depending on what scan level you select, you can select from the following
options to modify scan performance:
- Full Port Scan - Scans all ports (10000+ tcp, 2700+ udp) versus common ports (500+ tcp, 60+ udp). Useful for detecting services running on either common ports or non-standard ports.
- Exhaustive Scan - Runs a more thorough scan, but may cause the scan to take more time. Examples include checking for default router passwords on non-standard telnet ports, checking for Web application vulnerabilities in non-standard directories, checking for proxy vulnerabilities on non-standard HTTP ports, and checking for Oracle and Sybase vulnerabilities on all unidentified ports.
- Perform Dangerous Tests - The assessment will include dangerous checks, in which certain vulnerability exploits are launched in order to confirm that the end-system is or is not vulnerable. These tests may help eliminate false alarms by verifying the existence of certain vulnerabilities, but can cause services on the end-systems to crash as a result. Another side-effect of dangerous tests is that successful detection of a vulnerability could cause other vulnerabilities to be missed. That is, if a test crashes a service on the end-system, then any further tests against that service will come up negative. End-systems should be re-scanned after the known vulnerabilities have been fixed in case there are other vulnerabilities that were missed because the service crashed. If this option is not selected, then the assessment will skip these dangerous tests, and will report a potential problem if there is a possibility that the vulnerability exists.
- Authentication
- In order to conduct the most thorough and accurate scan possible,
the agent-less assessment gives you the
option of authenticating to target end-systems. Authentication allows
the assessment to access the registry,
file attributes, or package lists on the remote target. There are two benefits to
authentication. First, an authenticated scan is able to detect additional vulnerabilities,
such as client vulnerabilities and missing hot fixes, which could not otherwise be
detected by probing network services. Second, an authenticated scan is sometimes able to
check for fixes whose presence could not otherwise be determined, thereby reducing false alarms.
If you choose not to authenticate, the assessment will still conduct its
full set of unprivileged vulnerability checks, omitting only those few
which require authentication.
If you wish to run an authenticated assessment, enter a valid login and password in this section:
- Windows Domain Administrator - Do not enter the domain name
in the login field. The agent-less assessment will automatically
authenticate to the domain that the end-system is a member of. For example, if you are
scanning Host1 and Host2, and Host1 and Host2 are members of Domain_A, then
the assessment will authenticate
with Domain_A. If you also scan Host3, and Host3 is a member of Domain_B, then
the assessment will use the
provided password to authenticate with Domain_B when scanning that target. If a target is not a
member of a domain, the assessment will assume the given account is a
local account on each target. To use a
local account even if the end-system is a member of a domain, specify the account name as "local:login",
where login is the login name. Do not put a space after the colon.
Keep in mind that the assessment's detection of Windows updates should be used as a baseline assessment only. The assessment detects Windows updates using simple checks for the presence of registry keys and file time stamps, which cannot always account for updates which have been incorrectly installed, uninstalled, rendered ineffective due to incorrect order of installation, or other unusual situations. For more thorough evaluation of Windows updates, it would be advisable to use one of several available patch management tools.CAUTION: The encrypted Windows authentication functions require the crypto library which comes with OpenSSL. If the OpenSSL libraries are missing or outdated on the scanning system, a warning message will appear when the assessment starts, and passwords will be sent over the network in clear text. - SSH Login - For authentication to Linux, Unix, and Macintosh end-systems, any active user account on the system may be used. The SSH service must be running on the remote end-system in order for authentication to function.
- SNMP Communities - SNMP runs on routers and switches, as well as some printers, servers, and workstations. SNMP access is controlled using community strings and provides configuration information which could be used for improved host detection and vulnerability detection. Enter a comma-separated list of community strings that the assessment can use for SNMP access. It is not necessary to include default strings such as "public" and "private."
- Windows Domain Administrator - Do not enter the domain name
in the login field. The agent-less assessment will automatically
authenticate to the domain that the end-system is a member of. For example, if you are
scanning Host1 and Host2, and Host1 and Host2 are members of Domain_A, then
the assessment will authenticate
with Domain_A. If you also scan Host3, and Host3 is a member of Domain_B, then
the assessment will use the
provided password to authenticate with Domain_B when scanning that target. If a target is not a
member of a domain, the assessment will assume the given account is a
local account on each target. To use a
local account even if the end-system is a member of a domain, specify the account name as "local:login",
where login is the login name. Do not put a space after the colon.
- Test Set Assessment Resources
- Define which assessment servers you want to have perform the assessments.
- Use Onboard Assessment - Use the onboard agent-less assessment server.
- Load Balance All - Balance the assessment load across all of the agent-less assessment servers on the network.
- Use Assessment Server Pool - As a more granular
approach, you can specify an assessment server pool. For example, if you
have four agent-less assessment servers, you can put server A and server B
in server pool 1, and server C and server D in server pool 2. Then, you
can specify which server pool the configuration should use.
 Use the configuration menu button to:
Use the configuration menu button to:
- Add - Open the Add Assessment Server Pool window where you can add a new server pool.
- Edit - Open the Edit Assessment Server Pool window where you can edit the selected server pool.
- Used By - List all assessment test sets currently using the selected server pool.
- Manage - Open the Manage Assessment Server Pools window where you can view and define the assessment server pools that will be used in your assessment configurations.
- Assessment Delay
- This option allows you to delay the start of the assessment by the number of seconds specified.
For information on related windows: