The device Authentication tab enables you to configure and change the authentication settings on the selected device. Authentication must be configured and enabled on the device in order for individual port authentication settings to take effect (see How to Configure Ports).
To access this tab, select a device on the left panel's Network Elements tab, then click the Authentication tab in the right panel.
Click the graphic for more information.
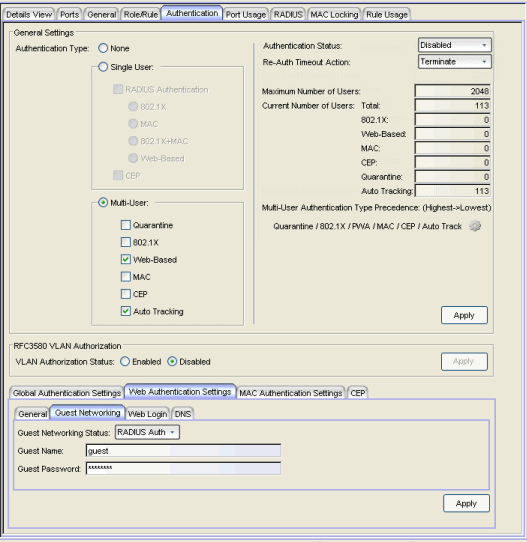
General Settings
- Authentication Type
- Select the appropriate single user or multi-user authentication types, or None. Only options supported by the
selected device will be available
for selection. Some devices support multiple authentication types and
multiple users (Multi-User Authentication) per port, while others are
restricted to only one or two authentication types and single users per
port (Single User Authentication). Deselect all options
to see what authentication types are supported by this device, or refer
to the NetSight Firmware Support tables for information on the
authentication types supported by each device type. When you choose an authentication type, the sections
unrelated to that type of authentication are
grayed out on
this tab and on the Port Properties Authentication Configuration tab
for the device's ports. If you choose None, authentication
of all types is disabled on the device. For more information on the
different types of authentication, see
Authentication Types.
WARNING: Switching Authentication Types, or changing the Authentication Status from Enabled to Disabled, will log off any currently authenticated users. NOTE: C2/B2 Devices. Because C2/B2 devices let you enable all three authentication types at the device level, use the Multi-User section to configure authentication types even though the device only supports a single user (and an optional IP phone) per port. The order in which authentication types are enabled at the device level may affect authentication settings that are already configured on the port. Because of this, it is important to configure authentication types at the device level first, and then configure your port-level authentication settings second.
If you are configuring a single user and an IP phone, be sure to set the port-level "number of users allowed" setting to 2. You can do this via the Port Configuration Wizard or the Port Properties Authentication Configuration tab, Authenticated User Counts subtab.
- Authentication Status
- If you've selected an authentication type other than None, you can
enable it here. The default is Disabled. Leaving Authentication Status
disabled gives you the ability to configure and reconfigure
authentication settings without affecting your network until
authentication configuration is complete. If you have selected multiple
authentication types, all of the authentication types selected will be
enabled or disabled with this one setting.
CAUTION: Setting the authentication status to Enabled will affect communications through the front panel ports. Any front panel port being used for management should be set to inactive/default mode before setting authentication status to Enabled. If you select the Enabled button, an Authentication Status window appears, offering you choices for actions that will take effect on front panel ports when authentication status is enabled. These options are described in detail on the Authentication Status window. (If you choose the Select Ports to set to Inactive/Default Role option, the Set Authentication Port Mode to Inactive/Default Role window appears, where you can select the ports you wish to set to Inactive/Default Role.)
- Re-Auth Timeout Action
- This setting defines the action for sessions that need to be re-authenticated if the RADIUS server re-authentication request times out. Select the Terminate option to terminate the session or the None option to allow the current session to continue without disruption.
- Maximum Number of Users
- For devices with Multi-User as their configured authentication type. The maximum number of users that can be actively authenticated or have authentications in progress at one time on this device. You can specify the maximum number of users per port on the port's Port Properties Authentication Configuration tab.
- Current Number of Users
- For devices with Multi-User as their configured authentication type. The current number of users that are actively authenticated or have authentications in progress, or that the device is keeping authentication termination information for. Any unauthenticated traffic on the port is not included in this count.
- Multi-User Authentication Type Precedence
- Displays the order in which the
authentication types will be tried on the device, with the
authentication type on the left having the highest precedence (it will
be tried first). You can edit the precedence order by clicking the Edit button
 . In the Edit Precedence window, select the authentication type you want to position,
and use the left or right arrow to arrange the types in the desired
order of precedence. The order determined here is also reflected in the
position of the options under Authentication Type.
. In the Edit Precedence window, select the authentication type you want to position,
and use the left or right arrow to arrange the types in the desired
order of precedence. The order determined here is also reflected in the
position of the options under Authentication Type.
| WARNING: | Leaving the default precedence is recommended. In particular, changing the Quarantine precedence to be lower than any other type or changing the Auto Track precedence to be higher than any other type can cause problems. |
| NOTE: | On E1 and E6/E7 devices, if both 802.1X and MAC authentication
are enabled, it is possible for the device to receive a start or response 802.1X
packet while a MAC authentication is in progress. If this happens, the device
immediately terminates the MAC authentication, and the 802.1X authentication
proceeds to completion. Regardless of the success of the 802.1X login attempt,
no new MAC authentication logins may occur on the port until 1) the link is
toggled; 2) the user executes an 802.1X logout; or 3) the 802.1X session is
terminated administratively. |
|---|
RFC3580 VLAN Authorization
RFC 3580 VLAN Authorization must be enabled on devices in networks where the RADIUS server has been configured to return a VLAN ID when a user authenticates. When RFC 3580 VLAN Authorization is enabled:
- devices that do not support policy, will tag packets with the VLAN ID.
- devices that do support policy and also support Authentication-Based VLAN to Role Mapping, will classify packets according to the role that the VLAN ID maps to.
You can also enable and disable VLAN Authorization at the port level using the Port Properties Authentication Configuration tab. If the device does not support RFC 3580, this section will be grayed out.
- VLAN Authorization Status
- Allows you to enable and disable RFC 3580 VLAN Authorization for the selected device.
Global Authentication Settings Tab
This tab lets you set session timeout and session idle timeout values for each authentication type.
Click the graphic for more information.
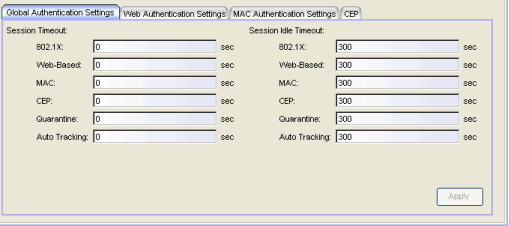
- Session Timeout
- The maximum number of seconds an authenticated session may last before automatic termination of the session. A value of zero indicates that no session timeout will be applied. This value may be superseded by a session timeout value provided by the authenticating server. For example, if a session is authenticated by a RADIUS server, that server may send a session timeout value in its authentication response.
| NOTE: | Non-zero values are rounded to the nearest non-zero multiple of 10 by the
device. |
|---|
- Session Idle Timeout
- The maximum number of consecutive seconds an authenticated session may be idle before automatic termination of the session. A value of zero indicates that no idle timeout will be applied. This value may be superseded by an idle timeout value provided by the authenticating server. For example, if a session is authenticated by a RADIUS server, that server may send an idle timeout value in its authentication response.
Web Authentication Settings Tab
For users of web-based authentication, this tab lets you specify web authentication parameters using four sub-tabs: General, Guest Networking, Web Login, and DNS.
General Tab
The General tab lets you specify the URL of the authentication web page and the IP address of the system where it resides. It also lets you enable certain web authentication features such as Enhanced Login Mode, on devices that support those features.
Click the graphic for more information.
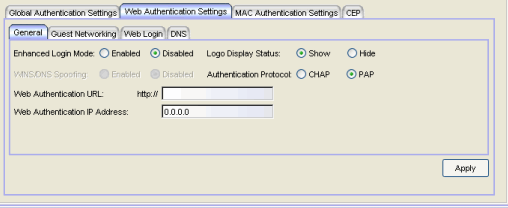
- Enhanced Login Mode
- Enabling the Enhanced Login Mode causes the authentication web page to be displayed regardless of whether the URL or IP address entered into the browser by the end user is the designated Web Authentication URL or IP address. This option is grayed out if the device does not support the mode.
- Logo Display Status
- Specifies whether the Extreme Networks logo is displayed or hidden on the authentication web page window. This option is grayed out if not supported by the device.
- WINS/DNS Spoofing
- Allows you to enable and disable WINS/DNS spoofing for the selected device. Spoofing allows the end user to resolve the Web Authentication URL name to the IP address using WINS/DNS. The default is Disabled. This option is grayed out if not supported by the device.
- Authentication Protocol
- Authentication protocol being used (PAP or CHAP). PAP (Password Authentication Protocol) provides an automated way for a PPP (Point-to Point Protocol) server to request the identity of user, and confirm it via a password. CHAP (Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol), the more secure of the two protocols, provides a similar function, except that the confirmation is accomplished using a challenge and response authentication dialog.
- Web Authentication URL
- URL for your authentication web page. Users wishing to receive network services access the web page from a browser using this URL. The http:// is supplied. Alphabetical characters, numerical characters and dashes are allowed as part of the URL, but dots are not. The URL needs to be mapped to the Web Authentication IP address in DNS or in the hosts file of each client. It must be resolvable via DNS/WINS, either on the device or at corporate, assuming the Web Authentication mapping has been set up on the corporate DNS/WINS service. This option is grayed out if not supported by the device.
- Web Authentication IP Address
- IP address of your authentication web page server. If you have specified a Web Authentication URL, the IP address needs to be mapped to the URL in DNS or in the hosts file of each client.
Guest Networking Tab
The Guest Networking tab lets you configure guest networking, a feature that allows any user to access the network and obtain a guest policy without having to know a username or password. The user accesses the authentication web page, where the username and password fields are automatically filled in, allowing them to log in as a guest. If the user does not want to log in as a guest, they can type in their valid username and password to log in.
| NOTE: | Guest networking is designed for networks using web-based authentication,
with port mode set to Active/Discard. |
|---|
Click the graphic for more information.
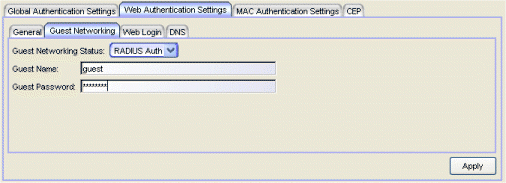
- Guest Networking Status
- Use the drop-down list to specify guest networking status:
- Disable -- Guest networking will be unavailable.
- Local Auth -- Guest Networking will be enabled. The user accesses the authentication web page where the username field is automatically filled in with the specified Guest Name. Once the user submits the web page using this guest name, the default policy of that port becomes the active policy. The port mode must be set to Active/Discard mode.
- RADIUS Auth -- Guest Networking will be enabled. The user accesses the authentication web page, where the username field is automatically filled in with the specified Guest Name, and the password field is masked out with asterisks. Once the user submits the web page using these credentials, the value of the Guest Password will be used for authentication. Following successful authentication from the RADIUS server, the port will apply the policy (role) returned from the RADIUS server. The port mode must be set to Active/Discard mode.
- Guest Name
- The username that Guest Networking will use to authenticate users. The guest name is displayed automatically on the authentication web page. If the user does not want to log in as a guest, they can type in their valid username to override the guest username.
- Guest Password
- The password that Guest Networking will use to authenticate users when RADIUS Auth is selected.
Web Login Tab
The Web Login tab allows you to customize the banner end users see at the top of the authentication web page and set a Redirect Time, if applicable.
Click the graphic for more information.
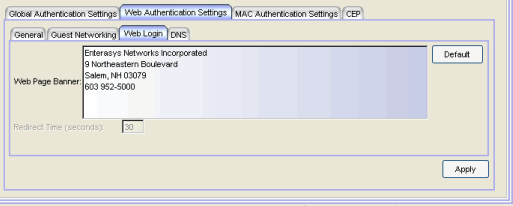
- Web Page Banner
- Use this area to create a banner that end users will see at the top of the
authentication web page. For example, you might include your company name and information
on what to do if the user has questions or problems. Because this banner also
appears in messages that occur during successful login and failed
authentication, as well as on the "Radius Busy" screen, it would not be
appropriate to include "Welcome to [Your Company]" in the banner.
The Default button allows you to reset the banner to default text provided in a text file (pwa_banner.txt). Initially, the default banner text is the Extreme Networks contact information. However, you can customize the text for your network by editing the pwa_banner.txt file, located in the top level of the Policy Manager install directory. Then, when you click the Default button, the new text will be displayed in the Web Page Banner area.
- Redirect Time
- For devices with Enhanced Login Mode
enabled. Specifies the amount of time (in seconds) before the end user
is redirected from the authentication web page to their requested URL.
An endstation using DHCP requires time to transition from the temporary IP address issued by the authentication process to the official IP address issued by the network. Redirect Time specifies the amount of time allowed for the end station to complete this process and begin using its official IP address. The default value of 30 seconds is adequate for most networks; however, some networks may require a longer or shorter time period. If the Redirect Time is not long enough, the browser times out while attempting to load the requested URL. In networks that only use static IP addresses, a Redirect Time of 5 to 10 seconds is usually sufficient; a value of less than 5 seconds is not recommended.
For example, if a user (in Enhanced Login Mode and a Redirect Time of 30 seconds) enters the URL of "http://ExtremeNetworks.com", they will be presented the authentication web page. When the user successfully authenticates into the network, they will see a login success page that displays "Welcome to the Network. Completing network connections. You will be redirected to http://ExtremeNetworks.com in approximately 30 seconds".
- Default
- Resets the authentication web page banner text to the default text provided in the text file, pwa_banner.txt. The default banner text is the Extreme Networks contact information. However, you can customize the text for your network by editing the pwa_banner.txt file, located in the top level of the Policy Manager install directory. Clicking Default also sets the Redirect Time field to the default value of 30 seconds.
DNS Tab
The DNS tab lets you add your DNS domain name and server addresses to support the Enhanced Login Mode on Matrix E1 devices. Enhanced Login Mode must be enabled in order to use this tab. The DNS servers are used to resolve URLs to IP addresses.
Click the graphic for more information.
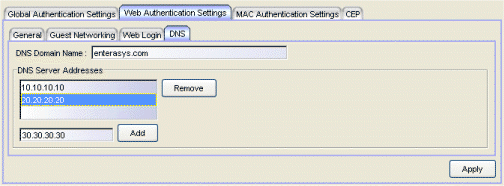
- DNS Server Addresses
- List your local DNS Server Addresses. Enter an IP address and click Add to add a server address. Select an address and click Remove to remove an address from the list. Addresses are used in the order they are listed.
MAC Authentication Settings Tab
This tab enables you to set up the MAC password for MAC authentication. In order for MAC authentication to work, you must also configure the RADIUS server with the MAC password as well as the MAC addresses which are allowed to authenticate.
Click the graphic for more information.
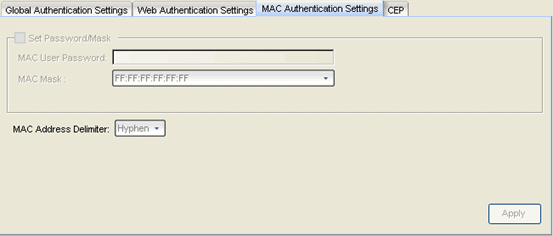
- MAC User Password
- The password that is passed to the RADIUS server for MAC authentication (1-32 characters).
- MAC Mask
- You can select a mask to provide a way to authenticate end stations based on a portion of their MAC address. For example, you could specify a mask that would base authentication on the manufacturers ID portion of the MAC address. The MAC Mask is passed to the RADIUS server for authentication after the primary attempt to authenticate using the full MAC address fails.
- MAC Address Delimiter
- The character used between octets in a MAC address:
-
- None — No delimiter is used in the MAC address (e.g. xxxxxxxxxxxx).
- Hyphen — A hyphen is used as a delimiter in the MAC address (e.g. xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx).
CEP Tab
This tab provides a way to identify Convergence End Points (IP phones) that are connecting to the device, and apply a role to the endpoint based on the type of endpoint detected. The CEP Detection sub-tab lets you create detection rules for identifying the endpoints, and the CEP Role Mappings sub-tab lets you map a role to each CEP product type.
| TIP: | You can configure CEP for multiple devices
using the Device Configuration Wizard. |
|---|
In addition to configuring CEP on the device, you must also enable CEP protocols on each port using the CEP Access sub-tab in the Port Properties Authentication Configuration Tab or the Port Configuration Wizard. Once you have configured CEP on the device and each port, you can monitor CEP usage on the Port Usage Tab (Port) or Port Usage Tab (Device).
CEP Role Mappings Tab
This tab lets you select the CEP product types supported on the device, and map a role for each type. Then, when a convergence endpoint (such as an IP phone) connects to the network, the device identifies the type of endpoint (using CEP detection rules) and applies the assigned role.
Click the graphic for more information.
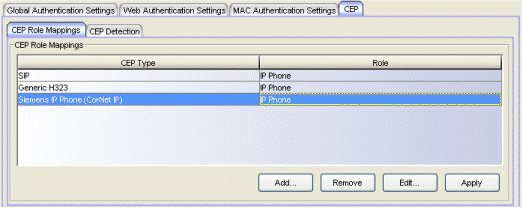
- CEP Role Mappings
- Lists the CEP types supported by the device and the role mapped to each type. Click Add to add a CEP type and role to the list.
- Add
- Opens the Add CEP Mapping window where you can select a CEP product type supported on the device, and map a role for that type. Your selections will be added to the CEP Role Mappings list.
- Edit
- To edit a CEP type in the CEP Role Mappings list, select the type and click Edit. The Edit CEP Mapping window opens where you can select a different CEP type and/or role.
CEP Detection Tab
Use this tab to create CEP detection rules that are used to determine if a connecting end-system is a CEP device, and what type of CEP device it is. This allows Policy Manager to assign the appropriate role to the port based on the type of CEP device detected.
| NOTE: | CEP detection rules apply only to Siemens, H.323, and SIP (Session Initiation
Protocol) phone detection. Cisco
detection uses CiscoDP as its detection method. |
|---|
CEP detection rules are based on two detection methods:
- TCP/UDP Port Number detection - Many CEP vendors use specific TCP/UDP port numbers for call setup on their IP phones. You can create detection rules that identify CEP devices based on specific TCP/UDP port numbers. By default, Siemens Hi-Path phones will be detected on TCP/UDP port 4060.
- IP Address detection - H.323 phones use a reserved IP multicast address and UDP port number for call setup. You can create detection rules that will detect an IP phone based on its IP address in combination with an IP address mask. By default, H.323 phones will be detected using the multicast address 224.0.1.41 and the TCP/UDP ports 1718, 1719, and 1720. SIP phones will be detected using the multicast address 224.0.1.75 and the TCP/UDP port 5060. H.323 and SIP phones will also be detected using only their respective multicast addresses without the TCP/UDP ports.
Click the graphic for more information.
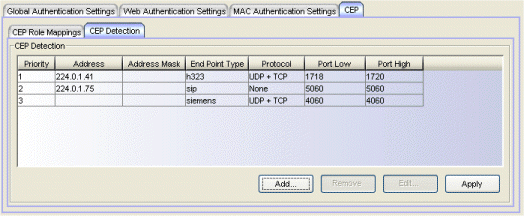
- Priority
- The rule priority with one (1) being the highest priority. The rule with the highest priority will be used first, so it is recommended that the highest priority be given to the predominate protocol in the network to provide for greater efficiency.
- Address
- If the rule is based on IP address detection, this field displays the IP address
that incoming packets will be matched against. By default, H.323 will use
224.0.1.41 as its IP address, SIP will use 224.0.1.75 as its IP address, and Siemens will have no IP address configured.
- Address Mask
- If the rule is based on IP address detection, this field displays the IP address mask that incoming packets will be matched against.
- End Point Type
- Specifies the endpoint type that will be assigned (H.323, Siemens, or SIP) if incoming packets match this rule.
- Protocol
- If the rule is based on TCP/UDP port detection, this field displays the
protocol type used for matching, using a port range defined with the Port
Low and Port High values:
- UDP + TCP - Match the port number for both UDP and TCP frames.
- TCP - Match the port number only for TCP frames.
- UDP - Match the port number only for UDP frames.
- Add
- Opens the Add CEP Detection Rule window where you can create CEP detection rules.
- Edit
- To edit a CEP detection rule, select the rule and click Edit. The Edit CEP Detection Rule window opens where you edit the rule's parameters. You can also double-click an entry in the table to open the edit window.
For information on related tasks: